判断语句/分支语句 1.if else 和 if else if else语句
2.switch case语句
//if语句
/*
格式:if(条件){
语句;
}else if(条件){
语句;
}else{
语句;
}
*/
输入年龄进行范围判断
<body><input type="text" name="age"><input type="button" id="btn" value="提交"><script>
var btn = document.querySelector('#btn');
btn.onclick = function () {
let age = parseInt(document.querySelector('input[name="age"]').value);
if (age < 18) {
console.log("未成年");
} else if (age <= 35) {
console.log("中年");
} else {
console.log("老年人");
}
}
</script></body>
判断语句:switch case
//switch语句
/*
意思:根据表达式的值匹配不同的case分支并执行相应的代码
格式:switch(表达式的值){
case 比较的值:
执行的语句;
break;
···
default:
执行的语句;
}
*/
根据今天周几进行更换背景颜色
var date = new Date();var weekday = date.getDay(); switch (weekday) {
case 0:
console.log("7");
break;
case 1:
console.log("1");
break;
case 2:
console.log("2");
break;
case 3:
console.log("3");
break;
case 4:
console.log("4");
break;
case 5:
console.log("5");
break;
default:
console.log("6");
}
colorselect = ["red", "green", "yellow", "blue", "purple", "pink"];document.body.style.backgroundColor = colorselect[weekday];
循环语句/遍历语句
1.while循环
2.for循环
循环语句:while
//while语句
/*
格式:
while(条件){
语句;
}
*/
//示例一:
var liList = ["guohan","gh","gg","hh"];
var num = 0;
while (num<liList.length){
console.log(liList[num++]);
/*
console.log(liList[num]);
num++;
*/
}
//示例二:
var number = 1;
while(number<=10){
console.log(number++);
}
循环语句:for
//for循环
/*
//三种格式:
1.循环代替while:
for(变量初始化;判断条件;步进器){
语句;
}
2.遍历数组成员的下标或对象属性
for(变量(成员下标)in 数组){
语句;
}
3.遍历数组成员的值或对象属性的值
for(变量(成员的值) of 数组){
语句;
}
*/
补充:forEach(数组的内置方法): 遍历数组的每个元素并对每个元素进行一次指定的函数(回调函数)
//数组.forEach((当前元素,当前下标,原数组)=>{函数代码语句;});
var obj = ["guohan","gh","gg","hh"];
obj.forEach((item,key)=>{console.log(item)}) //数组.forEach((当前元素,当前下标,原数组)=>{函数代码语句;});//里面是匿名函数新写法
//obj.forEach(item=>{console.log(item)});
异常处理和主动抛出异常
//异常处理
1.抛出内置异常
格式:
try{
代码;
}catch(e){
代码; //如:console.log(`异常类型:${e.name},异常原因:${e.message}`);
}
2.主动抛出自定义异常
//自定义异常用函数定义
function 自定义异常函数名(message){
this.name = "(自定义的错误类型)";
this.message = message || ”默认信息错误"; //后面是防止 throw时忘记传入错误信息参数
}
try {
// 可能抛出异常的代码(包含 throw)
if (条件不满足) {
throw 自定义异常函数名(message); // 主动抛出异常
}
// 正常逻辑(如果没抛异常,会执行这里)
} catch (error) {
// 捕获到异常后执行的处理逻辑
console.error("捕获到异常:", error.message);
} finally {
// 可选:无论是否抛出异常,都会执行的代码(如清理操作)
console.log("操作结束");
}
*/
抛出异常:
//抛出内置异常
try{
console.log(num);
}catch(e){
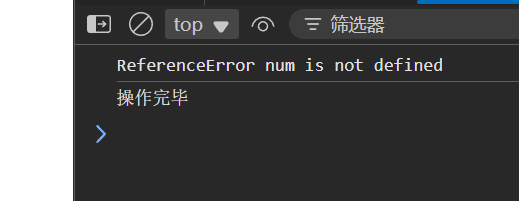
console.log(e.name,e.message); //e.name:异常类型 e.message:异常原因
}finally{
console.log("操作完毕")
}
//主动抛出自定义异常 throw
try {
console.log(num);
} catch (e) {
console.log(`异常类型=${e.name},异常原因=${e.message}`); //异常类型=ReferenceError,异常原因=num is not defined
}
//主动抛出自定义异常 throw
function UserError(message) {
this.name = "userException";
this.message = message || "默认错误信息";
}
Person = {"name": "guohan", "age": 17};
try{
if (Person.age < 18){
throw new UserError("未成年禁止进入");
}
console.log("可以进入");
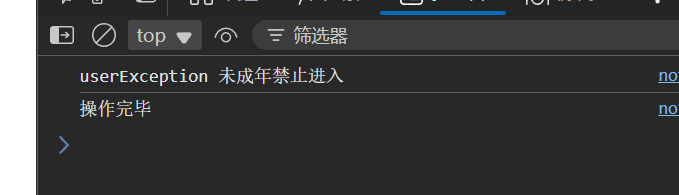
}catch(e){
console.log(e.name,e.message);
}finally{
console.log("操作完毕");
}
与python区别:

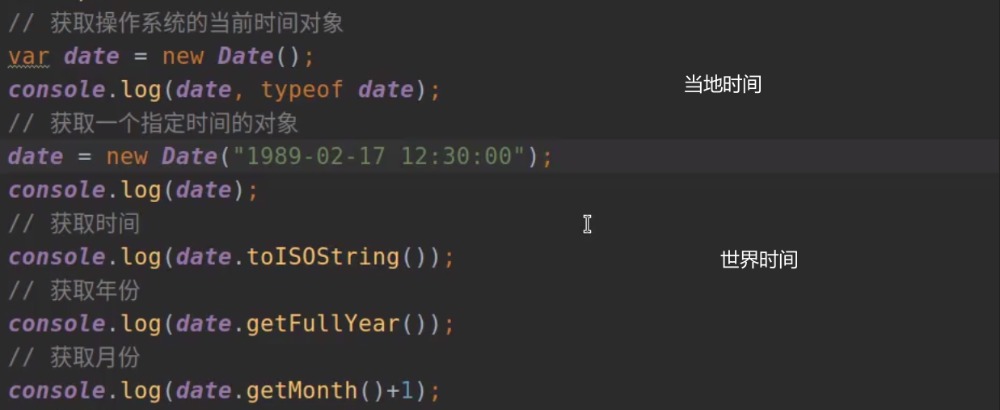
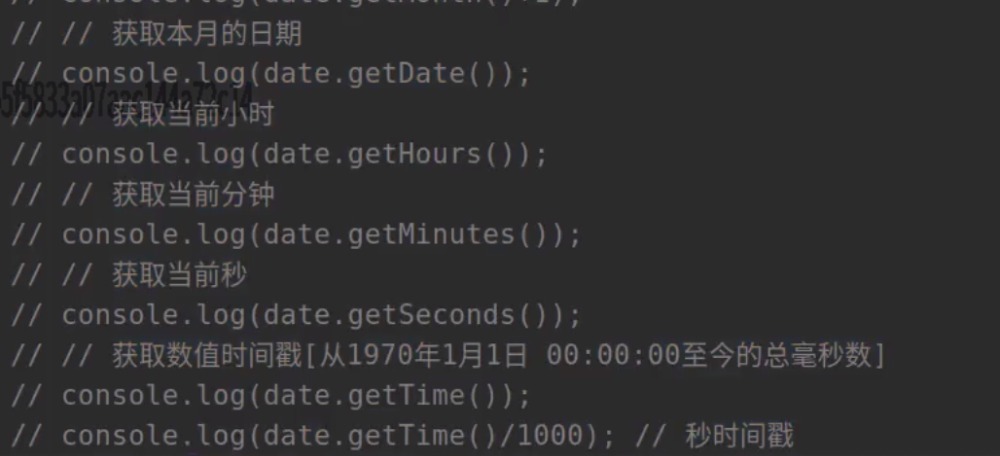
时间相关:
该文章在 2025/11/1 9:27:18 编辑过
